2019 Sep 03
(contd.) 2019 Sep 10
SciCen 706
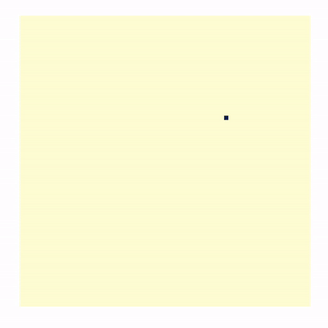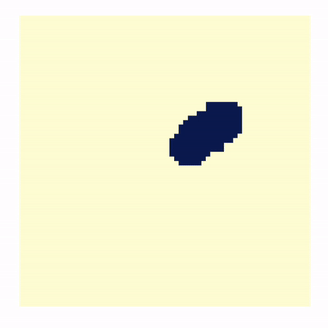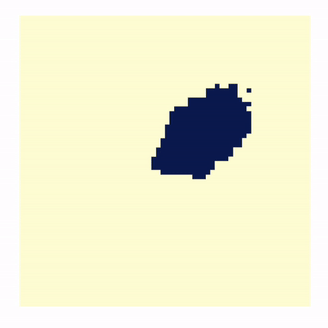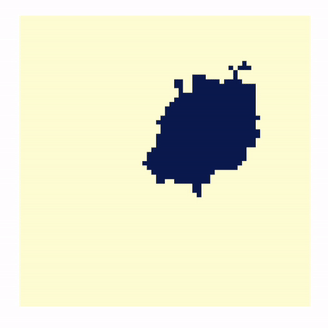
- Defining Regions that Contain Complex Astronomical Structures
- Abstract: Astronomers are interested in
delineating boundaries of extended sources in noisy images. An
example is finding outlines of a jet in a distant quasar. This
is particularly difficult for jets in high redshift, X-ray
images where there are a limited number of pixel counts. Using
Low-counts Image Reconstruction and Analysis (LIRA), McKeough
2016 and Stein 2015 propose and apply a method where jets are
detected using previously defined regions of interest (ROI).
LIRA, a Bayesian multi-scale image reconstruction, has been
tremendously successful in analyzing low count images and
extracting noisy structure. However, we do not always have
supplementary information to predetermine ROI and the size and
shape can greatly affect flux/luminosity. LIRA is also unaware
of correlations that may exist between adjacent pixels in the
real image. In order to group similar pixels, we impose a
successor or post-model on the output of LIRA. We adopt the
Ising model as a prior on assigning the pixels to either the
background or the ROI. The final boundary and uncertainty are
informed by the posterior draws of these assignments. This
method has been applied to the jet data as well as simulations
and appears to be capable of picking out meaningful ROIs.
- jit.si/CHASC1993 [webcast url] (connect with desktop browser [Chrome works best] or dedicated mobile app)
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
 [animated gif]
[animated gif]
- jit.si/CHASC1993 [webcast url] (connect with desktop browser [Chrome works best] or dedicated mobile app)
2019 Oct 01
SciCen 706
- An Information Theory Approach on Deciding Spectroscopic Follow Ups
- Abstract:
Classification and characterization of variable phenomena and
transient phenomena are critical for astrophysics and
cosmology. These objects are commonly studied using
photometric time series or spectroscopic data. Given that many
ongoing and future surveys are in time-domain and given that
adding spectra provide further insights but requires more
observational resources, it would be valuable to know which
objects should we prioritize to have spectrum in addition to
time series. We propose a methodology in a probabilistic
setting that determines a-priory which objects are worth
taking spectrum so that classification prediction is improved.
Objects for which we query spectrum are reclassified using
their full spectrum information. We first train two
classifiers, one that uses photometric data and another that
uses photometric and spectroscopic data together. Then for
each photometric object we estimate the probability of each
possible spectrum outcome. We combine these models in various
probabilistic frameworks (strategies) which are used to guide
the selection of follow up observations. The best strategy
depends on the intended use. For a given number of objects
(127, equal to $5\%$ of the dataset) to be observed, we
improve 37\% (47) class prediction accuracy as opposed to 20%
(25) of a non-naive (non-random) best base-line strategy.
Further, we improve the ground truth probability 1.18 times as
much as the best base-line strategy. Our approach provides a
general framework for follow-up strategies and can be extended
beyond classification and to include other forms of follow-ups
beyond spectroscopy.
- jit.si/CHASC-19-10-1 [webcast url] (connect with desktop browser [Chrome works best] or dedicated mobile app)
- Presentation slides:
gdrive [ppt]
download [pdf] - jit.si/CHASC-19-10-1 [webcast url] (connect with desktop browser [Chrome works best] or dedicated mobile app)
2019 Oct 08
SciCen 706
- Projects of RISE-AstroStat II
- Abstract: Current challenges in the analysis of
astronomical data include the development of efficient source
detection algorithms. This includes images, as well as, multi
dimensional data with spectral and/or timing information.
Although major progress has been made in these directions over
the past years, significant work is needed in order to apply
these method to the next generation of X-ray, and
multi-wavelength data. I will present some of these challenges
and how they are linked to the ASTROSTAT-II project, a network
of European, US, and Canadian Astronomy and/or Statistics
institutes.
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2019 Oct 22
SciCen 706
- The Devil's in the Details: Photometric Biases in Modern Surveys
- Abstract: Many modern surveys use
maximum-likelihood estimates (MLEs) for positions, fluxes, and
other parameters for stars, galaxies, and other astrophysical
phenomena from 2-D images. These MLEs are then used to make
catalogs used in the vast majority of astronomical analyses. I
will provide an overview of the basic ingredients present when
modeling these images, and illustrate how the MLE behaves in
various cases. I will then present results from recent work
showing that the MLE systematically overestimates the flux as
a function of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the number
of parameters involved in the fit. I will then examine how
this bias behaves when fitting multiple images at once, which
are necessary to estimate the "colors" of astronomical
objects. We find that common "forced" photometry approaches
(where the position is sometimes fixed) actually compound the
above bias in derived colors, while more rigorous "joint"
photometry approaches (where all images are modeled
simultaneously) actually distribute the bias between all the
images. We find our bias is present when examining data from
idealized simulations, fake object pipeline tests, and real
astronomical datasets, implying it is widespread among most
datasets in use today. I will also discuss second-order
effects relating to error estimation.
- Presentation Slides [.pdf]
- See also: arXiv:1902.02374 [url]
- Presentation Slides [.pdf]
2019 Oct 29
12:30pm-1:30pm EDT
Room 101, Center for Integrated Life Sciences & Engineering,
610 Commonwealth Ave, Boston
- Astrostatistics: The Intersection of Statistics and Outer Space
- In observation of World Statistics Day, the 50th anniversary of the moon landing, and the first images of a black hole, the BU Student Chapter of the American Statistical Association is hosting a seminar featuring scientists from the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard and Smithsonian. The presenters will discuss general statistical issues in X-ray analysis and then focus on data issues specific to calibration in spectral and image data.
- Co-sponsors:
Boston Chapter of the American Statistical Association
BU Spark! & the Hariri Institute for Computing- Live stream at https://bostonu.zoom.us/j/422150563 [zoom]
- Presentation slides:
Aneta Siemiginowska [.key]
Vinay Kashyap [.pdf]
Xiao-Li Meng [.pdf] - Co-sponsors:
2019 Nov 5
Crete
- Automated characterization of galaxy morphologies
- Abstract: The morphological appearance of a galaxy is one of the most direct indicators of its evolutionary history. This is why morphological classification labelling and parametrisation are fundamental information to account for when constructing a galaxy sample. Incoming surveys performed via LSST and EUCLID will yield data for unprecedented sample sizes: it is therefore vital to automate classification procedures.
One common and simple approach to classify morphologies in large samples is to summarize a galaxy's appearance via parametric fitting.
Moving to smaller scales, we are interested in the detection/characterization of morphological sub-structures of galaxies. We present our preliminary pipeline for the automated detection and parametrization of galaxy-merger features such as tidal tails and shells.- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2019 Nov 12
SciCen 706
- Mapping, Transport and Diffusion: A Energetic Variational Approach
- Abstract:
In this talk, I will introduce some analytical techniques to study the dynamics and equilibrium of complicated systems, such as those in transport and diffusion. The main ingredient is to introduce a unified energetic variational approach in order to capture various couplings and constraints.
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2019 Nov 19
SciCen 706
- Inferring the ACIS sub-pixel grade distribution
- Abstract:
The active layer in the CCD detectors consists of silicon. When an X-ray
photon is absorbed in that silicon layer, it causes a cloud of free
electrons. While this electron cloud drifts towards the gate electrodes,
it spreads. In the CCD detectors on Chandra, the electron cloud is
typically big enough to span several pixels when it reaches the "bottom"
of the silicon layer. Thus, every detected event does not only give us
an integer pixel location, but the signal in a number of pixels. The
"grade" is a way to encode this spatial pattern into a single number. If
a photon hits the center of a pixel, the electron cloud might fit
entirely into that pixel, but if it hits near the corner, the electron
cloud is likely to overlap multiple pixels.
In order to perform accurate simulations of Chandra data, we need to know the probability distribution of grades, given a sub-pixel location and energy. In this talk, I will introduce the problem, and lay out my idea for an approach to reconstruct that distribution from observed data and show some initial (not satisfying) fits. I am asking for advice on better methods to reconstruct the sub-pixel grade distribution.
In principle, a solution to this problem could also improve our understanding of pile-up, a long standing problem in Chandra data analysis.- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2019 Dec 17
SciCen 706
- Large Scale Kriging: A High Performance Multi-Level Computational Mathematics Approach
- Abstract:
Large scale kriging problems usually become numerically expensive and
unstable to solve as the number of observations are increased. In this
talk we introduce techniques from Computational Applied Mathematics
(CAM), Partial Differential Equations (PDEs), and High Performance
Computing (HPC) to efficiently estimate the covariance function
parameters and compute the best unbiased predictor with high
accuracy. Our approach is based on multi-level spaces that have been
successful in solving PDEs. The first advantage is that the estimation
problem is decoupled and the covariance parameters are efficiently and
accurately solved. In addition, the covariance matrix of the
multi-level spaces exhibit fast decay and is significantly better conditioned
than the original covariance matrix. Furthermore, we show that the
prediction problem can be remapped into a numerically stable form
without any loss of accuracy. We demonstrate our approach on test
problems of up to 512,000 observations with a Matern covariance
function and flexible placements of the observations on a single CPU core.
Many of these test examples are numerically unstable and hard to solve.
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2020 Jan 21
12:30pm EST
M-240, 160 Concord
- LIRA/Ising Updates
2020 Jan 28
SciCen 706
- STROOPWAFEL: a Dutch cookie and an adaptive sampling algorithm to simulate rare outcomes from astrophysical populations
- Abstract:
Gravitational-wave observations of binary black hole mergers are rapidly providing new insights into the physics of massive stars and the evolution of binary systems. Making the most of expected near-future observations for understanding stellar physics will rely on comparisons with binary population synthesis models. However, the vast majority of simulated binaries never produce binary black hole mergers, which makes calculating such populations computationally inefficient.
In this meeting I will present our adaptive importance sampling algorithm, STROOPWAFEL, that we wrote to improve the computational sampling efficiency of population studies of rare events. I will present its performance compared to traditional Monte Carlo sampling from the birth distributions and will discuss the similarities of the code with playing the board game battleships.
At the end of the presentation I will discuss some statistical challenges that we are currently facing in our effort to further optimize the STROOPWAFEL code, for which I would love to get some input from the audience. Stroopwafels will be provided.- Broekgaarden et al. 2019, MNRAS 490, 5228 [ADS]
- data [zenodo]
- code [github]
- Presentation slides: [.pdf] ; [github] ; [.pptx]
- Broekgaarden et al. 2019, MNRAS 490, 5228 [ADS]
2020 Feb 25
Imperial
- Domain Adaptation and Covariate Shift - A Literature Review
- Abstract: In supervised statistical machine learning tasks, learning algorithms are trained on categorized training objects with the aim of generalizing the classification by making predictions on unlabeled target objects. If the labeled training data is not an accurate representation of the target data distribution, learning algorithms will not predict the unlabeled samples well.
In this talk, I will present a review of general methods proposed in the machine learning community to overcome this issue - known as domain adaptation, transfer learning, covariate shift and sample selection bias.
The review will then be extended to domain adaptation methods applied to astronomical data. One particular case of selection bias in supervised training on astronomical sources is the photometric classification of supernovae type Ia, based on spectroscopically confirmed training samples. Propensity scores, a well-established methodology in causal inference, have successfully been proposed and will be reviewed in this context.
I would like to conclude with a discussion about extensions of the methods to related fields, e.g. active learning, semi-supervised learning and further potential applications on astronomical data sources.- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2020 Mar 03
SciCen 706
- Adaptive Methods for Time-Modulated Stars
- Abstract:
In this paper we focus on Long Period Variable (LPV) and
Blazhko stars, both characterized by slowly time-varying (or
simply time-modulated) parameters: mean, amplitude, period and
phase. Miras are a typical example of LPV stars, with an
average mean period ranging from 100 to 1,000 days and large
amplitudes of light variation of more than 2.5 magnitudes
visually and more than 1 magnitude in the 5 infrared
wavelengths. The period of these stars is a very useful
indicator of their size and luminosity as well as their age,
mode of pulsation and their overall evolution. Previous
research has revealed some important correlations between the
period and other parameters such as amplitude, mass loss and
IR excess due to dust surrounding the star. The magnitude of
LPV exhibits a (possibly quadratic) timevarying mean, as well
as time-varying amplitude and period. The Blazhko effect,
which is sometimes called long-period modulation, is a
variation in period, amplitude or phase in RR Lyrae type
variable stars. The amplitude-modulated pulsation of RR Lyrae
stars has a strong periodic component with an often observed
variation on a longer time scale. The amplitude variation is
accompanied by phase changes of the same period. The
modulation period can be anywhere between 10 and 700 days,
without any correlation with the fundamental period. The
Blazhko effect is a periodic amplitude and/or phase modulation
shown by some 20-30% of the galactic RRab stars. Our goals are
modeling and forecasting these light curves. In our approach
we allow for a smooth time-varying trend, as well as for
smooth time-varying coefficients describing the local (in
time) amplitudes of the cosine and sine waves. Our approach is
flexible because it avoids assumptions about the functional
form of trend and amplitudes. More precisely, we propose a
semi-parametric model where only part of the model is
time-varying. The estimation of our time-varying curves
translates into the estimation of time-invariant parameters
that can be performed by ordinary least-squares, with the
following two advantages: modeling and forecasting can be
implemented in a parametric fashion, and we are able to cope
with missing observations.
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
2020 Mar 10
SciCen 706
- Modeling our Milky Way Galaxy using Astrostatistics, Big Data, and Data Visualization
- Abstract: Mapping our Milky Way is hindered by
the Sun's unfortunate vantage point inside its disk, and by
the challenges of converting 2D integrated "on the sky"
measurements into 3D views of our Galaxy. In this talk, I will
discuss how we can combine publicly available data on the
colors of stars with new stellar distance measurements from
Gaia to map the 3D distribution and properties of stars and
interstellar material ("dust") which forms them. Specifically,
I will discuss the Bayesian inference framework which
underpins our star and dust modeling, and compare the accuracy
of our approach to much more expensive techniques based on
radio observations. Finally, I will discuss how leveraging the
latest data visualization software in combination with our new
3D measurements has revealed the existence of a new
Galactic-scale structural feature of our Milky Way Galaxy,
which takes the peculiar form of an undulating sine wave.
- Presentation slides: [.pdf] ; [.key]
- Presentation slides: [.pdf] ; [.key]
24 Mar
Skype
- On Concordance
- Calibration concordance project discussion: status, extension.
21 Apr
Penn State
- Time Delay Cosmography Toward the Hubble Constant Estimation: Past, Present, and Future.
- Abstract: The Hubble constant is a core cosmological parameter that represents the current expansion rate of the Universe. One way (out of many) to infer this quantity is to use strong gravitational lensing, i.e., an effect that multiple images of an astronomical object (e.g., a quasar) appear in the sky. This effect occurs when the trajectories of the light (from the object to the Earth) are bent by a strong gravitational field of an intervening galaxy. Strong gravitational lensing produces two types of the data; (i) multiple brightness time series data of the gravitationally-lensed images and (ii) pixel-wise image data of the lens and lensed object. The former is used to infer time delays between the arrival times of the multiply-lensed images (arXiv 1602.01462) and the latter is used to estimate gravitational potential that the lensed images pass through (arXiv 1801.01506). These two components are used to infer the Hubble constant via physical equations. In this talk, I overview the project, explaining what we have done and what we want to do in the future.
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
- Presentation slides [.pdf]
Xufei Wang (Harvard)
19 May
Remote
- Flare Onset Evolution in Solar Active Regions
- Solar flares are known to be distributed as a power-law over several magnitudes of released energy in a process of flare release that is best described as a scale-free self-organized critical process. We explore variations and limitations in the power-law description over the solar cycle and identify a trend in how individual active regions evolve.
- Slides [.pdf]
- BAAS235 220.01 [iPoster]
- Slides [.pdf]
- Power law analysis for total energy data
- The total energy of solar flare follows a distribution with uni-modal density and obeys power law in a range which is on the right of the mode, yet the range is unknown and hence needs to be estimated. This poses a rather intriguing and unique estimation problem that apparently has not been studied in the statistical literature. The unique nature of this problem prompted us to use the underutilized maximum product of spacings method to fit the cumulative distribution function, which maximizes the product of the spacings.
- Slides [.pdf]
- Slides [.pdf]
9 June
Davis
- Modeling the graph segmentation with Fourier descriptors and quantifying the uncertainty of segmented astronomical figures
- Abstract: This talk will report our ongoing work of quantifying the uncertainty of object boundaries obtained by image segmentation. To obtain a manageable and yet flexible representation of object boundaries, we first apply Fourier descriptors to the segmented object of interest. We then employ the bootstrap methodology to assess the variability produced by the segmentation. We will illustrate how our method can be used to test if objects in two images are statistically different.
This is joint work with Vinay Kashyap, Thomas Lee, and Andreas Zezas.
Josh Ingram (New College of Florida and CfA)
7 July
Remote
- Maximum Product of Spacings: Power-law Distribution Point Estimation and Confidence Region
- Abstract: The presentation will recap the maximum product of spacings methodology, then discuss how to estimate the power-law region for solar flare data in detail. The talk will also share the recent work on how to build confidence region by treating product of spacings as the pivotal quantity, and illustrate the idea with a simple example.
- Maximum Product of Spacings: Power-law Characterizations of Solar Flares
- Abstract: Solar flare total energy, duration, and peak flux follow a power-law within an unknown region to the right of the mode of the distributions. The variations in the estimated distributions are compared across more than twenty years and two solar cycles using data from the GOES satellites. To fit the region, normalization constant, and exponent of the power-law distributions, the maximum product of spacings method is used.
- Presentation slides: Xufei Wang; Josh Ingram [.pdf]
- Presentation slides: Xufei Wang; Josh Ingram [.pdf]